OKR Cycle: Phases and Best Practices
Introduction
The OKR (Objectives and Key Results) framework is a powerful tool for setting and achieving goals in organizations of all sizes. Whether you're part of a startup, a mid-sized company, or a corporate giant, OKRs provide a structured approach to driving performance and success. To effectively harness the potential of OKRs, it's essential to understand the OKR cycle, the steps involved, and best practices for implementation. In this article, we'll explore the OKR cycle, it’s phases, and provide insights into how you can make the most of this strategy.
Understanding the OKR Cycle
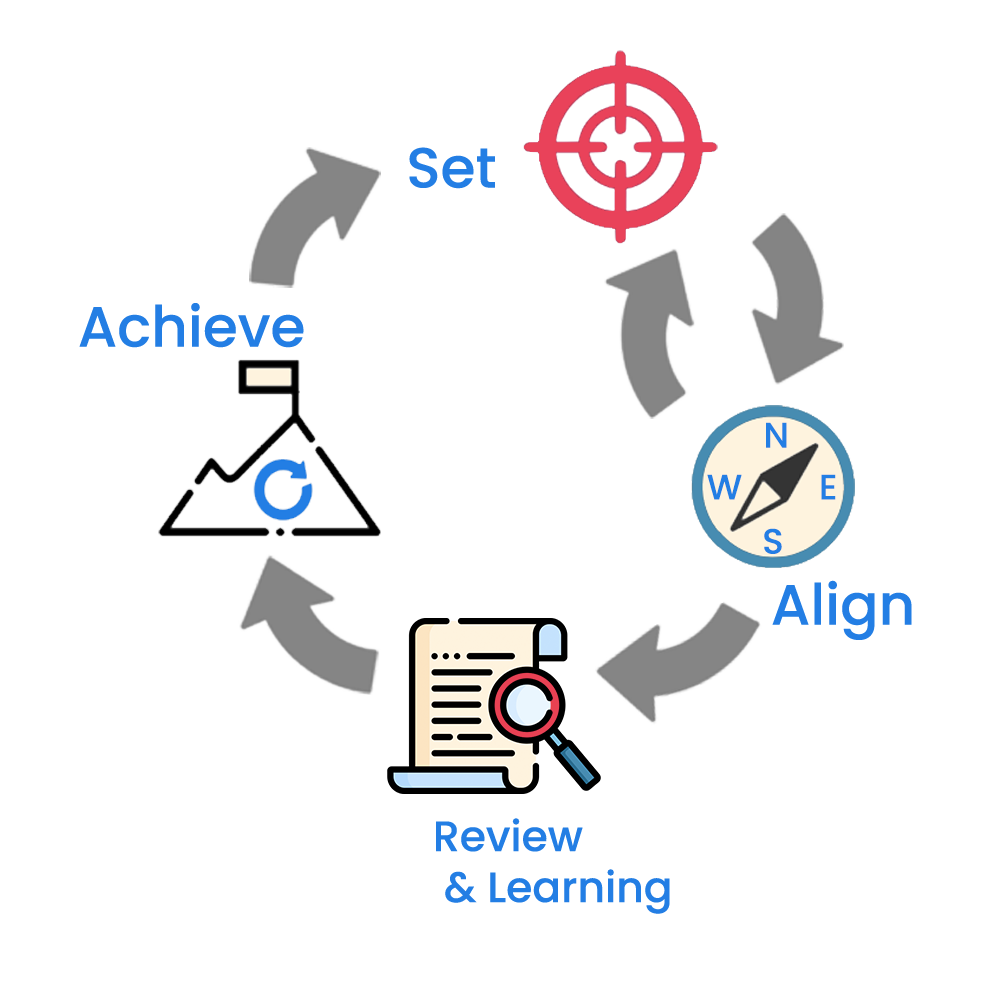
The OKR cycle is a recurring, time-bound process that organizations use to define, track, and achieve their objectives. It typically follows a quarterly schedule, but some organizations choose different time frames to suit their needs. The OKR cycle consists of several key phases:
- Planning: The cycle begins with the planning phase, often initiated at the start of a year or quarter. The planning phase begins with the leadership team setting high level organizational level strategic goals for the upcoming year and/or period which provides a clear sense of direction for the entire organization. Strategic objectives should be ambitious, actionable, and aligned with the organization's overall mission and vision. Well-crafted strategic objectives have the power to inspire and motivate teams. They should be more than just numbers or targets; they should be meaningful and resonate with employees at all levels. Once these organization’s strategic objectives are set, teams and individuals can start to develop their own OKRs. Similar to Strategic goals, encourage teams and individuals to set ambitious but achievable OKRs, and these OKRs should be aligned with the overall strategic goals of the organization. The planning phase is an opportunity to reflect on past performance and learn from it. Or
ganizations should assess what worked and what didn't in previous cycles, using this insight to refine their approach. - Alignment: This alignment is a key factor in the success of the OKR framework. Once OKRs have been developed, it is important to align them across the organization. This phase involves aligning team and individual goals with the top-level objectives to ensure that everyone is working towards a common purpose.This means communicating OKRs to all stakeholders and ensuring that everyone understands their role in achieving them. Alignment can be done through workshops, team meetings, and one-on-one conversations. The alignment phase serves as the bridge between high-level organizational objectives and the objectives set at the team and individual levels. It ensures that there is coherence and consistency in what different parts of the organization are working on. It fosters a culture of collaboration and transparency. Teams are encouraged to communicate and collaborate to ensure that their objectives support and complement those set at the organizational level.
- Execution: The execution phase is where the hard work begins and strategy is transformed into tangible actions. It's the stage where the work is put into motion, and teams and individuals start executing their plans to achieve the set objectives. This phase is pivotal for turning aspirations into concrete achievements. It's the time when teams and individuals take ownership of their assigned objectives and work diligently to meet the key results. During this phase, it is important to track progress regularly and make adjustments as needed. Regular check-ins and tracking are essential to the OKR cycle. By tracking key results and monitoring progress, organizations can assess their performance in real-time. This allows them to make timely adjustments and optimizations. Teams and individuals measure their key results and assign a score or confidence to indicate their progress. This step helps identify areas that need improvement and ensures accountability.
- Review and Learning: The Review and Learning phase is the final but crucial step in the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) cycle. It's the stage where organizations assess their performance, gain insights from their achievements and challenges, and use this knowledge to refine their approach for the next cycle. This phase is instrumental in the continuous improvement of an organization's goal-setting and execution processes. It provides valuable insights that can be used to refine the approach for the next cycle. This is a time to reflect on what went well, what could have been improved, and what lessons can be learned for the next quarter.
Best Practices for the OKR Cycle
To make the most of the OKR framework, consider these best practices:
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Include key stakeholders from different levels and departments in the planning phase. Their insights can help in creating objectives that are relevant and aligned with the organization's strategic vision.
- Keep Objectives Clear and Ambitious: Objectives should be easy to understand and ambitious but attainable. They should inspire and motivate teams.
- Select Key Results Thoughtfully: Choose key results that are specific, measurable, time-bound, and directly linked to the objectives. They should be indicators of success, not just tasks.
- Focus on Quality Over Quantity: It's better to have a few well-defined OKRs than a long list of vague ones. Quality over quantity is the key to effective OKRs.
- Top-Down Communication: Leadership should clearly communicate high-level objectives to all teams and individuals. This top-down communication provides a foundation for alignment.
- Engage Teams: Involve team leaders and managers in the alignment process. They play a pivotal role in ensuring that their teams' objectives support the organizational goals.
- Alignment Meetings: Hold alignment meetings where teams and individuals present their proposed OKRs. These meetings allow for feedback and adjustments as needed.
- Key Result Ownership: Clearly define who is responsible for each key result. Designate individuals or teams who will actively work towards achieving these results.
- Regular Check-Ins: Ensure that teams and individuals have regular check-ins to review progress and make necessary adjustments. Communication is essential for success.
- Transparency and Accountability: Make OKRs and progress visible to the entire organization. This transparency fosters accountability and alignment.
- Continuous Learning: Embrace a culture of continuous learning. Celebrate successes and learn from failures to improve the OKR process.
- Flexibility: Be open to adjusting OKRs if circumstances change during the cycle. Flexibility is crucial for adapting to evolving business needs.
- Feedback and Collaboration: Involve all teams and individuals in the review process. Encourage open discussions and gather feedback on what could be done differently.
- Refining Strategies: Use the insights gained to refine organizational strategies. Ensure that high-level objectives are more precise and that key results are challenging yet attainable.
Conclusion
The OKR cycle is a dynamic and iterative process that helps organizations set and achieve their goals. By following the steps and best practices outlined in this article, you can maximize the effectiveness of the OKR framework and drive improved performance and success within your organization. Whether you're a startup striving for rapid growth or a well-established company looking to enhance performance, OKRs can be a valuable tool in your strategic arsenal