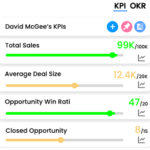
Key Performance Indicators Examples

Expansion Revenue
Expansion Revenue is a metric used to measure the increase in revenue resulting from expanding the customer base or increasing the frequency or value of purchases by existing customers.
There are a few different ways to calculate Expansion Revenue, but a common formula is:
Expansion Revenue = (New Revenue from Existing Customers – Previous Revenue from Existing Customers) + (New Revenue from New Customers – Acquisition Cost of New Customers)
- “New Revenue from Existing Customers” refers to the additional revenue generated from existing customers through upselling, cross-selling, or increased purchase frequency.
- “Previous Revenue from Existing Customers” refers to the revenue generated from existing customers prior to the expansion efforts.
- “New Revenue from New Customers” refers to the revenue generated from new customers acquired through expansion efforts.
- “Acquisition Cost of New Customers” refers to the cost incurred to acquire the new customers.
For example, if a company generated $100,000 in revenue from existing customers prior to expansion efforts, and generated an additional $50,000 in revenue from existing customers through expansion efforts, and acquired $200,000 in new revenue from new customers with an acquisition cost of $100,000, the Expansion Revenue would be ($50,000 – $100,000) + ($200,000 – $100,000) = $150,000.
It’s important to note that Expansion Revenue is a relative metric and should be considered along with other metrics such as customer acquisition cost (CAC) and customer lifetime value (CLV) to evaluate the overall effectiveness of the expansion efforts.
Measure what matters for your business with KPIs
Track business performance with real time key metrics against targets in one place without the need for multiple dashboards or reports